Carbon Credit Tokenization: Transforming Climate Action with Blockchain
I've always had interest in blockchain technology, so as a cool fun research project, we embarked on a journey to explore its potential applications in addressing pressing global challenges. Given the urgency of climate change and the need for innovative solutions, we delved into the realm of carbon credit tokenization.
Background
In the global fight against climate change, the emergence of carbon credits has been a pivotal strategy, particularly highlighted by agreements such as the Paris Agreement and frameworks like the Kyoto Protocol. Carbon credits function as tradable certificates representing the right to emit a specific amount of carbon dioxide or its equivalent greenhouse gases.
Current Carbon Credit Ecosystem
The current carbon credit ecosystem involves various stakeholders, including project developers, brokers, traders, and end buyers. Project developers create carbon credits through decarbonization projects, which are then traded through intermediaries to end buyers, typically large companies seeking to offset their carbon emissions.
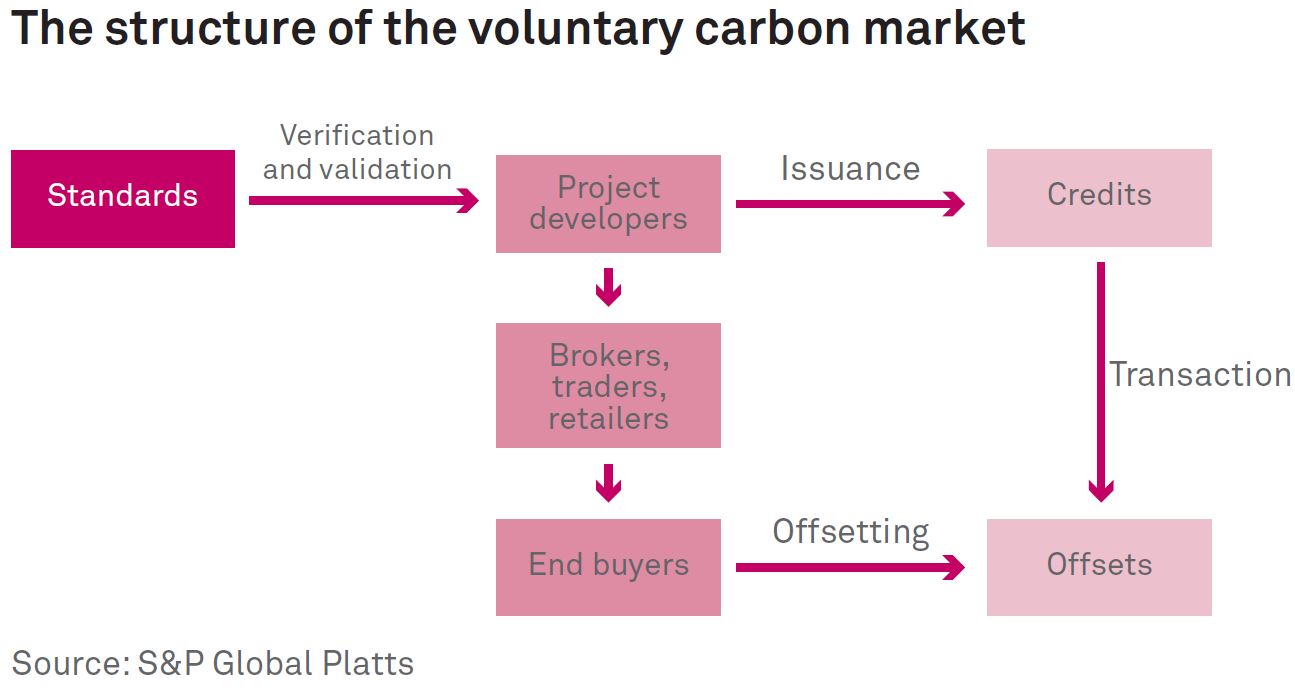
Stucture of current carbon market
Problems of the Current Carbon Credit System
- Verification Issues: Fragmented verification processes and varying standards lead to uncertainty and reduced legitimacy.
- Standardization Challenges: Lack of standardization in calculating carbon credits undermines the effectiveness of the system.
- Third-Party Risks: Involvement of third-party brokers introduces risks of fraud and high transaction costs, reducing trust and transparency.
Consequences of Current Problems
The consequences of these challenges include reduced credibility, inefficiency, and a lack of integrity and transparency in the carbon credit market, hindering its effectiveness in combating climate change.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology for Carbon Credit Tokenization
- Removal of Intermediaries: Blockchain facilitates direct transactions between project developers and end buyers, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing transaction costs.
- Enhanced Transparency: The transparent and decentralized nature of blockchain enables the public to track carbon credit transactions and ensure the integrity of projects.
- Funding Opportunities: Tokenized carbon credits can attract funding from the consumer market and incentivize businesses to participate in carbon reduction projects.
Solutions of Carbon Credit Tokenization
To address verification challenges, existing standards like the Golden Standard can be applied to quantify carbon credits. Smart contracts can ensure transparency and traceability in transactions, while Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) offer a secure and tradable representation of carbon credits. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) can further streamline token transactions and promote active trading.
Limits
Challenges such as liquidity issues and the need for standardization pose limitations to the widespread adoption of carbon credit tokenization.
Conclusion
Carbon credit tokenization holds immense potential in revolutionizing the carbon credit market, making transactions more efficient, transparent, and accessible. While blockchain technology offers promising solutions, collaboration and standardization efforts are crucial for its successful implementation.
In summary, while challenges remain, the integration of blockchain technology into carbon credit systems offers a pathway towards more effective climate mitigation strategies and sustainable development goals.
You can read our written report here.

